Description
This intelligence report discusses SocGholish, a JavaScript downloader used by threat actors to deliver malware payloads disguised as fake browser updates. It analyzes the recent tactics, techniques, and procedures employed by threat groups like Evil Corp in compromising WordPress websites, fingerprinting user profiles, and directing victims to malicious domains hosting the fake updates. The report also explores potential payloads delivered through SocGholish, such as Cobalt Strike, Zloader, information stealers, remote access trojans, and ransomware.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, SocGholish stands out as a particularly insidious threat. This JavaScript-based malware framework has been active since at least 2017 and it's persistence and adaptability make it a significant concern for both individuals and organizations.
What is SocGholish?
Also known as FakeUpdates, SocGholish, is a JavaScript downloader malware typically distributed through compromised websites that masquarade as legitimate software update pages. When unsuspecting users visit these sites, they are tricked into downloading and executing malicious files, often in the form of .zip or .js files.
How SocGholish Work?
The primary method of distribution for SocGholish is through drive-by downloads. These downloads occur when users visit compromised websites that have been injected with malicious JavaScript. The script prompts users to download what appears to be a critical browser update. Once the user downloads and executes the file, the malware is installed on their system.
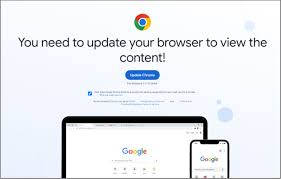
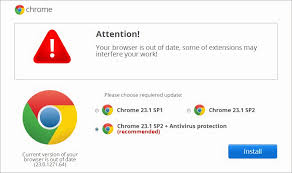
Once this malware is installed, SocGholish can download additional malware, including remote access trojans (RATs), information stealers and ransomware. This males it a versatile tool for cybercriminals who can use it to gain initial access to a system and then deploy other malicious payloads.
Techniques and Tactics
SocGholish employs several sophisticated techniques to evade detection and ensure successful infection:
- Domain Shadowing: Attackers use legitimare domains to host their malicious content, making it harder for security systems to detect the threat.
- Obfuscation: The JavaScript code is often obfuscated to prevent easy analysis and detection by security tools.
- Masquerading: The malware files are named to mimic legitimate software updates, increasing the likelihood that users will downlaod and execute them.
Impact and Associations
SecGholish has been linked to several high-profile cyberattacks and is often associated with ransomware groups like EvilCorp. It has also been used in conjunction with other malware campaigns, making it a significant threat in the cybercrime ecosystem.
Protecting Against SocGholish
To protect against SocGholish and similar threats, consider the following best practices:
-
- Regular Software Updates: Ensure that all software, especially browsers and plugins are kept up to date with the latest security patches from trusted sources.
-
- Use Security Software: Employ reputable antivirus and anti-malware solutions that can detect and block malicious scripts.
-
- Educate Users: Train users to recognize phishing attempts and the dangers of downloading software from untrusted sources.
-
- Monitor Network Traffic: Keep an eye on the network traffic for unusual activity that could indicate a compromise.
-
- Reputable/Verified Browser Extensions: Avoid using untrusted or unverified browser extensions.
Conclusion
SocGholish is a reminder of the constant vigilance required in the digital age. By understanding how this malware operates and taking proactive steps to secure systems, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves against this persistent threat.
Stay safe and stay informed!
More on SocGholish
https://www.gdatasoftware.com/blog/2024/07/37976-socgholish-fake-update
https://blog.sucuri.net/2022/08/socgholish-5-years-of-massive-website-infections.html
https://blog.sucuri.net/2024/03/new-wave-of-socgholish-infections-impersonates-wordpress-plugins.html
https://attack.mitre.org/software/S1124/
https://www.checkpoint.com/cyber-hub/threat-prevention/what-is-malware/socgholish-malware/

 }
}
 )
)